Protecting Network Continuity against WAN Outages
Enterprise WAN plays a key role as more enterprises today rely on it for operation. A high-speed and reliable internet connectivity is required for almost all business in the world. Some enterprises deploy multiple WAN architectures in an active/backup fashion, in which one may be an active link while the other stays idle as a backup link. This might result in inefficient utilization and waste of the bandwidth resource.
Outbound Failover & Load Balancing
> WAN Failover & Failback
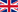
Network downtime means user frustration, lost productivity and decreased revenue. A short interruption can even have significant impacts such as dropped VoIP calls or disrupted application sessions. The major tasks for WAN failover is to help enterprises build a network that never fails. WAN failover ensures enterprise a unbreakable WAN connectivity in almost every situation.
By properly configuring automatic WAN failover on the appliance, the continuity for business networks is thus guaranteed. The mechanism works in conjunction with path monitoring, which constantly monitors the status on all WAN connections, and so is able to mark faulty links as inactive and remove them from the pool immediately. Traffic will then be sent across the remaining active paths as WAN failover automatically diverts traffic from the path(s) marked inactive. The mechanism of path monitoring continues to monitor the failed path(s) and marks them back active once they failback. WAN failover provides 99.99% network uptime, and maximizes business continuity and employee productivity for business.
Better WAN Efficiency through Load Balancing
> Outbound Load Balancing
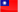
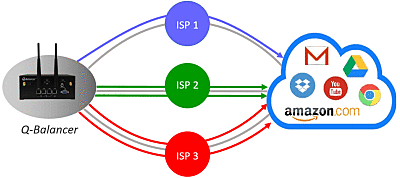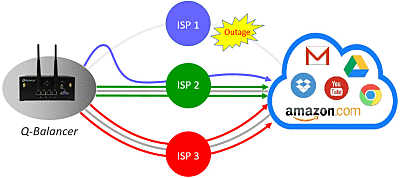
Outbound Load Balancing helps business cost-effectively build a reliable and fast connectivity through traffic distribution across available paths. A variety of algorithms are incorporated to help the appliance find the most active and responsive link(s) for traffic distribution. Like WAN failover, outbound load balancing works in conjunction with path-monitoring as well. Based on the measured result, the selected algorithm efficiently distributes traffic across available path(s) and avoids the paths which are either down or slow.
> Define Your Load Balancing Rules with The Following Algorithms
Routing Persistence
Persistently route traffic of a single session through the same path, and keep going until the session ends.
Round-Robin by IP
Distribute outgoing traffic across multiple paths in the method of round robin.
Weighted Round-Robin by IP
Distribute traffic across multiple paths by IP in accordance with the weight assigned on the WAN links.
ISP Response Time
Take the best path based on the response time from the target IP when the requests arise. ISP Response Time is suitable for the applications latency-sensitive.
Jitter
Take the best path based on the target IP or end-to-end round-trip time variation across the links when new requests arise. The algorithm is suitable for the applications that need low level of packet delay variation.
Uplink
Dispatch the requests in accordance with the uplink bandwidth availability, and traffic will be directed to the path with the most available uplink bandwidth.
Downlink
Dispatch the requests in accordance with the downlink bandwidth availability, and traffic will be directed to the path with the most available downlink bandwidth.
Bidirectional
Dispatch the requests in accordance with the bidirectional bandwidth availability, and traffic will be directed to the path with the most available bidirectional bandwidth.
Round-Robin by Connection
Distribute traffic across multiple paths based on the method of round robin when new requests arise.
Weighted Round-Robin by Connection
Distribute traffic across multiple paths based on the method of round robin in conjunction with the weight assigned to each of the paths when new requests arise.
Optimum Routing Path
Make use of response time, loading, and bandwidth availability to condition the optimum path when the requests arise.
Priority
Take the path with highest priority from the selected path(s), and takes the second-priority path only when the path with highest priority went down.
Tunnel Bonding
Distribute traffic across overlay tunnels by packets, providing a faster, more reliable and secure connectivity for business applications like VPNs and video conferencing.
Redirect
Redirect the selected type of outgoing traffic to specific IP hosts based routing policy.
The ability to harness WAN links enables enterprises to highly utilize the overall bandwidth resources. Better user experience will be delivered as the best-performing and least-loaded WAN connection(s) is always selected when new requests arise.
Top Benefits
> Increased network performance
> Minimal downtime with WAN redundancy
> Increased WAN scalability
> Improved productivity
> Cost saving by leveraging low-cost broadband technologies