Ensuring Incoming Requests to Internal Servers
Each host connected to the Internet has a unique IP address, with which the other devices can therefore find it. In reality, users access online information through human-readable domain names, like google.com or yahoo.com rather than IP address. It is like the phonebook of the Internet. When a DNS request is received by a DNS server, the DNS server then returns with the IP address of the domain name requested. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses, while web browsers interact with web servers through the IP addresses.
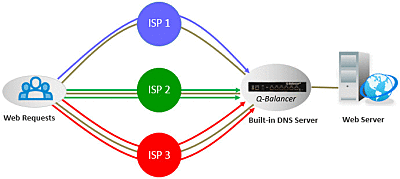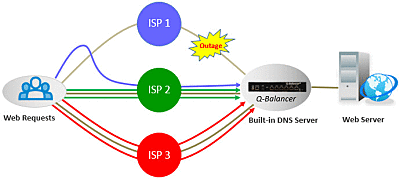
However, incoming requests would possibly not be able to access the hosted servers in case of a WAN failure as DNS is not able to detect WAN outages or congestion. It might return with the IP address from the failed WAN. Also, the finite bandwidth of a single uplink might become a bottleneck when the number of incoming requests increases.
> Inbound Failover & Load Balancing
Inbound Failover & Load Balancing
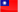
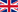
Connecting multiple WAN links and taking turn to reply DNS queries with IP addresses from different WAN links can possibly mitigate the issue. By doing so, the hosted servers then appear as a different IP address to each of the incoming DNS queries. However, there are still possibility to return with IP addresses from the faulty or congested WAN link(s).
Inbound load balancing of Q-Balancer is the solution to the issue. The appliance constantly checks the link status, and dynamically removes bad link(s) from its DNS table. It avoids the IP addresses from failed or congested link(s) when responding to DNS queries. Therefore, incoming requests are always directed to active path(s) or efficiently distributed across the available paths. This highly improves the availability and response of hosted services to incoming requests.
Q-Balancer is the best-in-class inbound load balancing solutions, and has been successfully deployed by lots of heavy-traffic enterprises in the world.
Top Benefits
> Avoiding service disruption caused by unexpected and planned downtime.
> Maximizing uplink utilization without complex configuration.
> Improved response times and maximize availability for hosted services.
> Flexibility to control WAN access for hosted services.